Moore’s Law states that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles about every two years. Say, the Kirin 990 5G chip has up to 10.3 billion transistors inside. At the same time, the Apple A13 has 8.5 billion transistors. We couldn’t find any data for the Snapdragon 865. But the Snapdragon 855 has around 6 billion transistors. These numbers sound quite astonishing. But they refer to the high-end mobile platforms. We mean it’s reasonable to see top-notch chips with the best performance and the latest innovations. But the mid-range smartphone market grabs the most of the customers. So we’d like to compare the latest mid-range SoCs in order to understand which of them provides the best performance. For this, we have chosen the Qualcomm Snapdragon 768G, the Huawei HiSilicon Kirin 820, and MediaTek Dimensity 820.
Each of these chips has its own advantages. But for an average user, they may be reflected only in the actual performance. So we will try not only to introduce their structure and novelties but also to explain what advantages they bring.
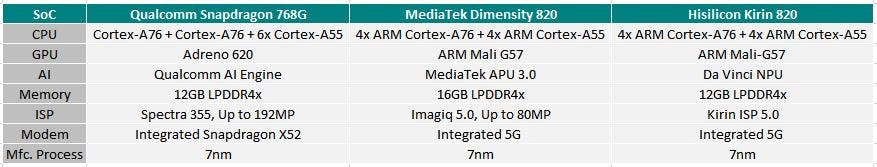
Snapdragon 768G vs Kirin 820 vs Dimensity 820
What’s a SoC?
In the past, we have been using a special phrase to define it – ‘a brain of a digital device or a computer’. Simply put, it was the CPU (Central Processing Unit). But the latter has been accompanied with various chips like GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), memory controllers, specialized video and audio chips (DSP), and many more. But now, all those parts are integrated into one chip. We call it a system-level integration. In this sense, SoC (System-on-a-Chip) means a single chip that includes a lot of different components and implements various functions.
SoC = CPU + GPU + memory controller + DSP + …
Now, we should also add the 5G modem to this list!
There are not many chip makers on the globe. Apart from Qualcomm, MediaTek, Huawei, and Samsung, we should also mention Xiaomi, which has released its first chip (Surge S1), and a couple of other Chinese smartphone brands that are working on their own chips.
As for graphics cards, there are 3 major manufacturers – ARM, Qualcomm, and Imagination. The former one comes in with Mali GPUs, the second vendor makes Adreno series GPUs, and the third one comes with PowerVR GPUs.
Snapdragon 768G
Well, it’s clear that the Snapdragon 768G is not anything new. This SoC is developed on the base of the Snapdragon 765 series. The main difference between these two is that the SND768G features a slightly overclocked ‘prime’ CPU code (@2.4GHz vs. 2.3GHz), a marginally overclocked GPU (15% speed binned Adreno 620), and supports for some of the company’s Snapdragon Elite gaming features.

It features the same Cortex-A76 cores in a 1+1 configuration (one Prime high-clocked core, and one medium clocked core), alongside 6 Cortex-A55 cores. As said, the main difference lies in the CPU performance. The big cores’ frequencies are now at up to 2.8GHz and 2.4GHz. They are responsible for the Performance. Simply put, when running heavy games or apps, in the peak situation, the chip will handle the tasks better and more easily.
Connectivity
The biggest advantage of the Snapdragon 765G (therefore, the Snapdragon 768G) is that it makes 5G globalization faster and smoother. This chip is based on a 7nm process node of TSMC. The 5G modem in this chip supports a peak download speed of up to 3.7Gbps and an upload speed of up to 1.6Gbps. the Snapdragon X52 modem inside, like the Snapdragon X55 modem, also supports all key 5G connectivity features such as mmWave, sub-6GHz, 5G SA and NSA modes, TDD and FDD bands with DSS, 5G roaming and multi-SIM support. In other words, it allows the chipset to connect to 5G networks in a larger number of areas. It supports Wi-Fi 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), Qualcomm aptX Adaptive Audio, Bluetooth v5.2, and USB Type-C (v3.1).
The Snapdragon 768G supports dual-frequency GNSS. It can result in more precise location tracking if the smartphone has a chip capable of supporting multiple frequencies (L1+L5 or E1+E5a). By the way, this is the first SND700 chip to come with such a functionality.
The Snapdragon 768G adopts Qualcomm’s AI engine and low-power Sensing Hub to give your device contextual awareness of voice commands. But this doesn’t mean it will drain your battery ruthlessly. The newer Hexagon Tensor Accelerator also helps the fifth-gen AI Engine to work more smoothly. Overall, the Snapdragon 765G SoC is capable of 5.5 TOPS (trillions of operations) performance, closing in on the Snapdragon 855’s 7 TOPS performance.
At the same time, a discrete component called the ‘Qualcomm Sensing Hub’ has also been announced. The Sensing Hub is designed for always-on detection of audio with support for multiple hotwords such as ‘Hey/Okay Google’ and ‘Alexa’.
Imaging
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 768G integrates a Spectra 355 image signal processor (ISP). It supports up to 192-megapixel camera capture. The SoC supports up to 120Hz full-HD+ displays and up to 60Hz QHD+ displays. The integrated ISP supports multi-camera capture. So the manufacturers can put various sensors such as primary, tele and wide-angle lenses. It’s also capable of capturing 4K HDR video too.
This SoC also comes with an Adreno 620 GPU. It’s improved by 15% on this SoC when compared to the Snapdragon 765G. The newer chip also supports Adreno updateable GPU drivers, the first 7-series platform to with the support. It has support for 120Hz displays as well. The Snapdragon 768G comes with Snapdragon Elite Gaming features for smoother gameplay and enhanced detail. It features same the Hexagon 696 digital signal processor (DSP) as the Snapdragon 765G. Qualcomm added support for HDR10+ and Dolby Vision video playback in the Adreno 620.
The Snapdragon 768G supports a memory capacity of up to 12GB! Even better, it supports memory speeds up to 2133MHz.
Qualcomm has added a new ‘Quick Charge AI’ technology. And though it doesn’t adds the charging speed, it will extend the longevity of your smartphone’s battery.
Phones powered by the Snapdragon 768G
Dimensity 820
Like the previous case, the Dimensity 820 is the successor of the Dimensity 800. But our protagonist brings faster CPU and GPU performance, supports for 120Hz panels, and has an improved ISP.

The Dimensity 820 is built on TSMC’s 7nm FinFET process and uses the same CPU microarchitecture as the previous SoC. There are eight ARM cores in a big.LITTLE arrangement. And though MediaTek was rather conservative about setting the clock speed of performance cores on the Dimensity 800, it is targeting much higher frequency this time around with all four ARM Cortex-A76 performance cores clocked at 2.6GHz. Just for comparison, the regular Dimensity 800 comes with a clock speed of up from 2.0GHz.
As for the graphics card, the Dimensity 820 utilizes a 5 core variant of the ARM Mali-G57 GPU. To provide an improved gaming experience, MediaTek has added its own HyerEngine 2.0. The latter brings a range of software-based enhancements for better graphics performance including intelligent allocation of CPU, GPU and memory, network latency optimizations, call and data concurrency, enhanced HDR visuals and more.
Imaging
As said above, among many improvements, the Dimensity 820 also supports high refresh rate panels. Though the Dimensity 800 supports high refresh panels as well, it can only handle FHD+ displays at a 90Hz refresh rate. In this sense, the Dimensity 820 supports FHD+ displays at up to 120Hz refresh rate. What we like more is the support for MiraVision display enhancement technology. The latter offers OEMs to implement various software-based features to improve the viewing experience. When saying enhancements, we mean the ability to upscale low-res content to Full HD, HDR10 Remapping, blue light filter, and brightness dimmer for better nighttime reading experience. Of course, we should also point out ClearMotion feature. It automatically converts standard 24/30fps content to 60 or 120fps on supported displays.
You should know, the Image Signal Processor (ISP) is called Imagiq at MediaTek. This time, we are dealing with the Imagiq 5.0. It supports up to 80MP camera sensors. This is not as attractive as on the Snapdragon 768G, but it’s still up from 64MP camera support on the Dimensity 800. The Imagiq 5.0 also promises Action Camera-grade Electronic Image Stabilization (EIS), multi-frame 4K HDR video recording, real-time video bokeh, and improved noise reduction.
Connectivity
Like all Dimensity series chips, the MediaTek Dimensity 820 also features an integrated 5G modem with support for both Standalone (SA) and Non-standalone (NSA) Sub-6GHz networks. The modem supports 5G Carrier Aggregation, dual SIM standby, Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), and Voice Over New Radio (VoNR) on both SIMs.
Phones powered by the Dimensity 820
Kirin 820
The Kirin 820 has become popular due to the 5G modem integrated in it. This allows the chip to support both non-standalone and standalone architectures as well as TDD/FDD full-frequency bands. So the phones powered by this chip can provide a stable 5G connectivity in most regions. To reduce latency, this chipset gets the industry-highest 5G network ratio by comprehensively accelerating 5G network searching and handover. It also quickens the time for processing large files and videos. We also would like to point out that the Kirin 820 supports bandwidth part (BWP) technology. The latter implements the flexible switching of bandwidth resources with available 5G bandwidths. As a result, it greatly reduces 5G energy consumption and offers a lasting 5G experience.

AI
Another eye-catching feature of this SoC is the Huawei’s Da Vinci NPU. It ensures an AI computing increase by 73%. At the same time, it provides a lower power consumption compared with its predecessor. Huawei is a leader in the field of on-device AI. So it’s not accidental that the Kirin 820 boasts of AI computing power. Generally, the HiAI platform with developers and partners enables and enriches the AI application ecosystem.
The Kirin 820 comes with an octa-core architecture and is based on a 7 nm process node. There are one high-performance big core, three balanced middle cores, and four energy-efficient little cores. As a result, the overall performance is improved by 27% compared with the previous generation. The big and middle cores are Cortex-A76 but come with a lot of customizations. At the same time, the little cores are customized based on Cortex-A55. As a result, the operating rate is up to 2.36 GHz.
Gaming
The Mali-G57 GPU inside comes with Kirin Gaming+ 2.0 technology. The latter is capable of boosting the performance by 38% and energy efficiency by 39%, enabling uninterrupted gaming experiences. The technology fuses GPU scheduling into the CPU and DDR system frequency modulation scheduling. Apart from this, Kirin Gaming+ 2.0 comes with a precise performance and power consumption model by tracking the game during the entire process. It learnes over 1 million frames of game images for refinements to performance and power consumption scheduling for each frame and in-depth and precise optimization
For the better photography, the chip integrates Huawei-developed ISP 5.0, which packs industry leading block-matching and 3D filtering (BM3D) image noise reduction, and dual-domain video noise reduction technologies to for clearer night-time photos.
Phones powered by the Kirin 820
Conclusion
Now, we can say that the Kirin 820 and Dimensity 820 are closer rivals. They integrate almost identical components set. So it’s assumed they will provide an identical performance. In this sense, the Snapdragon 768G has gone further and it seems it is a head higher than the rest two. But there are not many models powered by these chips. Once we get more, the conclusions on their performance will become more justified. At the moment, we can only say all three chipsets have been designed to bring 5G to larger masses. But they also allow manufacturer to add various high-end features. So all handsets powered by these chips can be considered as pseudo-flagship models.






As far as the specs are concerned, the Mediatek 5G chipset looks a lot better than the other two and a lot affordable too.