Microsoft started rolling out Windows 11 this week. As you know, the installation of a new software platform requires that the device used meets a number of requirements. If your computer does not meet them, then do not rush to get upset, because the developers from Microsoft themselves hace a method that will allow you to install the operating system on incompatible devices.
One of the common reasons for incompatibility is the requirement for the Trusted Platform Module 2.0. The TPM can be disabled in the BIOS, but older computers simply don’t have it. In terms of supported processors, Intel and AMD also have clear limitations that could hinder the installation of Windows 11. Fortunately, Microsoft does not seem to be going too far to prevent users of officially unsupported computers from interacting with the new OS.
The fact is that this week on the Microsoft support site there was an article for how to install Windows 11. In it, the developers described different options for installing a new OS, and also revealed how to download the system on unsupported computers. So, it turns out that for this it was enough to change just one registry parameter; as shown in the screenshot below.
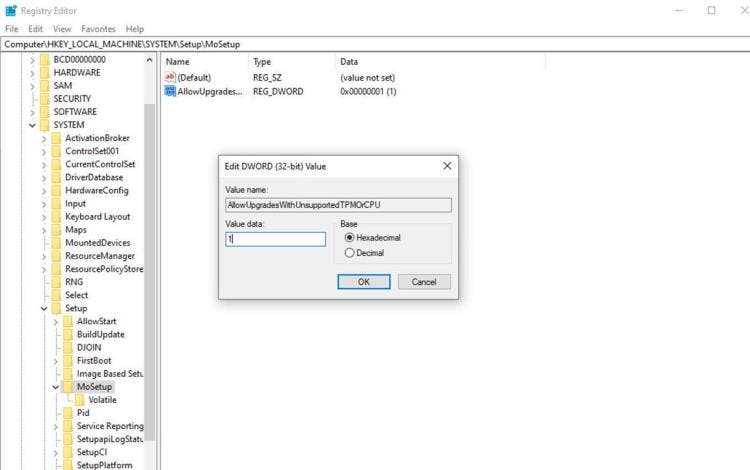
After making the appropriate adjustments, Windows 11 installation will not check for a working TPM 2.0 and a supported processor. However, this method requires TPM 1.2 to be avaialble. Microsoft also reminds us that it does not recommend installing Windows 11 on a device that does not meet the minimum system requirements; and the user, by doing this, acknowledges and understands the possible risks.
How to install Windows 11 on incompatible devices
On the Windows 11 software download page, select Create tool now and follow the instructions to install Windows 11.
- Microsoft recommends against installing Windows 11 on a device that does not meet the Windows 11 minimum system requirements. If you choose to install Windows 11 on a device that does not meet these requirements, and you acknowledge and understand the risks, you can create the following registry key values and bypass the check for TPM 2.0 (at least TPM 1.2 is required) and the CPU family and model.
- Registry Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup\MoSetup
- Name: AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPMOrCPU
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 1
-
Note: Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall the operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that it will have solutions to these problems. Modify the registry at your own risk.

