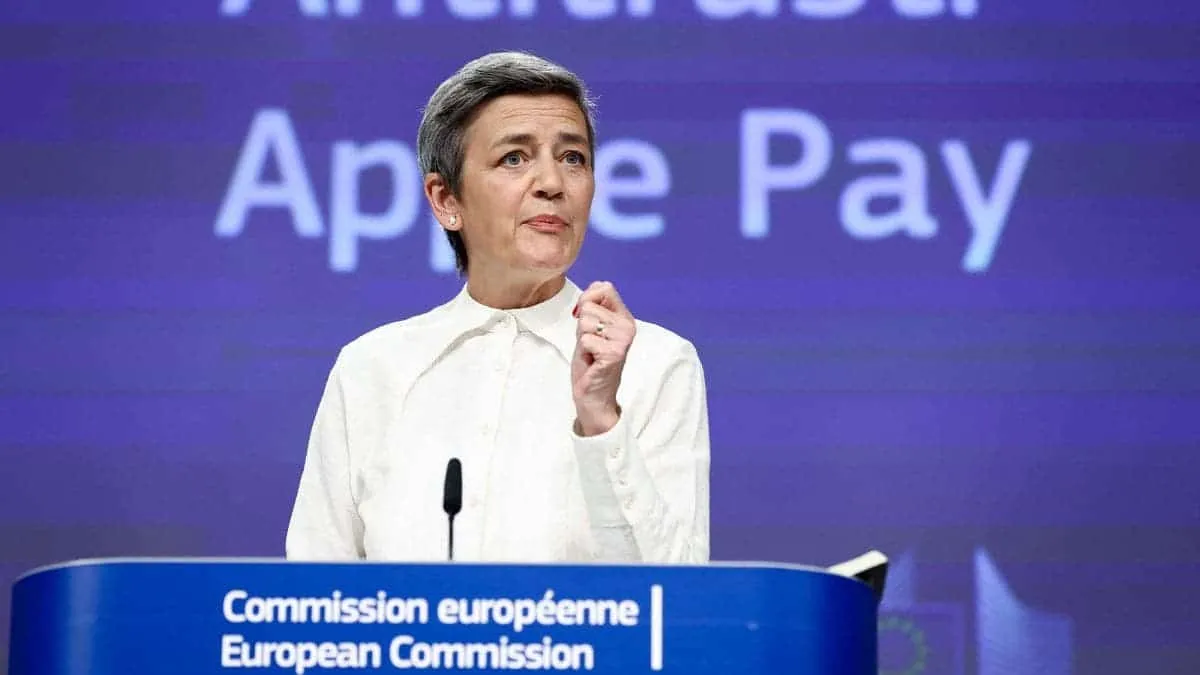
The European Union is too strict when it comes to the rights of its citizens and competition among various companies. In this sense, we should say that the EU is one of those rare regions that is actively struggling against tech giants – Apple, Google, Amazon, Facebook, etc. – and tries not to allow them to “swallow” relatively smaller companies. For instance, recently, the EU has been accusing Apple of its dominant position in mobile wallets on iOS. It has already sent Apple a formal “Statement of Objections” with the preliminary view. Thus, it started an antitrust proceeding.

“The Commission takes issue with the decision by Apple to prevent mobile wallets app developers, from accessing the necessary hardware and software (‘NFC input’) on its devices, to the benefit of its own solution, Apple Pay,” reads the decision. “Today’s Statement of Objections takes issue only with the access to NFC input by third-party developers of mobile wallets for payments in stores.”
What’s more important, Apple’s (and not only its) exclusionary behavior “leads to less innovation and less choice for consumers for mobile wallets on iPhones.”
This is only the This Is The Very Early Stage Of Antitrust Proceedings Against Apple
As this is the initial stage of the antitrust proceedings against Apple, the latter will have the opportunity to respond to the Commission’s list of objections. Moreover, as the EU mentioned a Statement of Objections “does not prejudge the outcome of an investigation.”
In fact, everything began much earlier. Last year, Apple was accused of unfairly penalizing rival music streaming services. Any government has the ability to levy fines. For instance, yesterday, we learned that Russia would file a case against the search engine and enforce a turnover fine of 7.2 billion rubles (about $0.1 billion). Of course, the EU can do the same as well. The fine could reach up to 10 percent of Apple’s global revenue ($36 billion). Plus, the EU can request the company to change its business practices. However, the charges will be much smaller.
Apart from this antitrust proceeding against Apple, a week earlier, the EU has passed two major legislative acts intended to counter the negative effects of digital tech giants. To start with, it’s the Digital Services Act (DSA). The latter forces various firms to control their content more tightly. Secondly, it’s the Digital Markets Act (DMA). This one ought to level the business playing field. In other words, due to it, the smaller companies should be able to compete with the largest corporations.
Popular News
Latest News
Loading