USB Type-C is becoming increasingly prevalent across various devices, including smartphones, laptops, headphones, and monitors. Its primary advantage lies in its versatility, as it can handle data transfer, video streaming, and power delivery all through a single cable. Nonetheless, this adaptability does introduce some complexity.
With the adoption of USB-C by Apple for its iPhone 15, we can confidently declare that we’ve entered the USB-C era. We have some helpful suggestions on how to make the most of these new ports on your laptop, smartphone, or tablet.
Everything you need to know about the USB-C port
What exactly is USB Type-C?
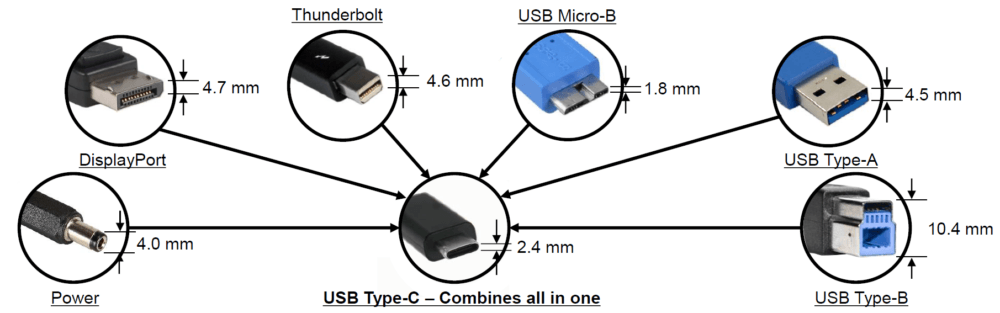
USB Type-C, often referred to as USB-C, is the universal connector promoted by USB-IF, the organization known for establishing USB transfer standards. It’s crucial to differentiate between USB-C, the connector itself, and USB, the data transfer standard (such as USB 2.0, USB 3, etc.). These two elements should not be confused.
The primary advantage of the USB-C port lies in its symmetrical design. It allows a cable to be inserted in either direction, eliminating the frustrations associated with previous USB ports and making it comparable to Apple‘s reversible Lightning connector (prior to the iPhone 15). Moreover, USB-C is closely associated with several exciting emerging technologies, including USB4, Thunderbolt 4, and USB Power Delivery.
It’s important to note that USB Type-C is not a new USB protocol standard. Instead, it is a new connector that can support USB, among other protocols like HDMI. Therefore, distinguishing between the connector, USB Type-C, and the data that flows through the cable is essential.
Think of the USB Type-C connector as a conduit, completely separate from the content flowing within it. Within this connector, various protocols can be transmitted for diverse purposes, including:
- Data:
- USB
- Thunderbolt
- Audio & Video
- DisplayPort Video Streams
- HDMI video streams
- Audio Stream (USB Audio)
- Energy:
- USB Power Delivery
- Proprietary technologies like OnePlus Dash Charge, Warp Charge, Huawei Super Charge, Qualcomm QuickCharge, etc.
What complicates matters is that the capabilities of USB-C ports can vary from one device to another. For instance, on some devices, USB Type-C ports may support specific USB protocol versions but not video or power protocols. To illustrate, a port might be USB Power Delivery certified but limited to USB 2.0 for data transfer. Similarly, a connector can handle USB 3.1 Gen 2 without the ability to transmit an HDMI stream or support USB Power Delivery.
This remarkable versatility has given rise to USB-C hubs, enabling the transformation of a laptop into a stationary workstation using a single cable.
Regrettably, there’s no guarantee regarding the functionality of the USB Type-C port on your smartphone. Therefore, it will be crucial for manufacturers to be transparent about what is possible and what is not. They can achieve this by clearly indicating the characteristics of the onboard USB Type-C port on product specifications or packaging.
USB-C 2.1 – What’s New?
In the year 2021, USB-IF introduced the USB-C 2.1 standard. It’s important to note that we’re still referring to the same reversible connector, but this update to the standard brings forth new capabilities. Remarkably, since it retains the same connector design, the new version maintains full backward compatibility.
Here are the key enhancements of the USB-C 2.1:
- Increased Charging Power: USB-C 2.1 empowers devices to charge at a much higher rate, now reaching up to 240 watts, as opposed to the previous limit of 100 watts.
- USB4 Support: With USB-C 2.1, there’s potential for compatibility with the USB4 protocol, opening the door to faster data transfers and improved performance.
- DisplayPort 2.0 Compatibility: USB-C 2.1 introduces support for DisplayPort 2.0, which can enhance the quality and capabilities of video output. Once again, it’s essential to note that these advancements are not automatic guarantees but rather optional possibilities contingent on having a compatible device and cable.
In essence, USB-C 2.1 expands the horizons of what this versatile connector can achieve, offering greater power delivery, improved data transfer capabilities, and enhanced display options, all while maintaining compatibility with older devices.
Data Transfer through USB-C: Navigating the Standards
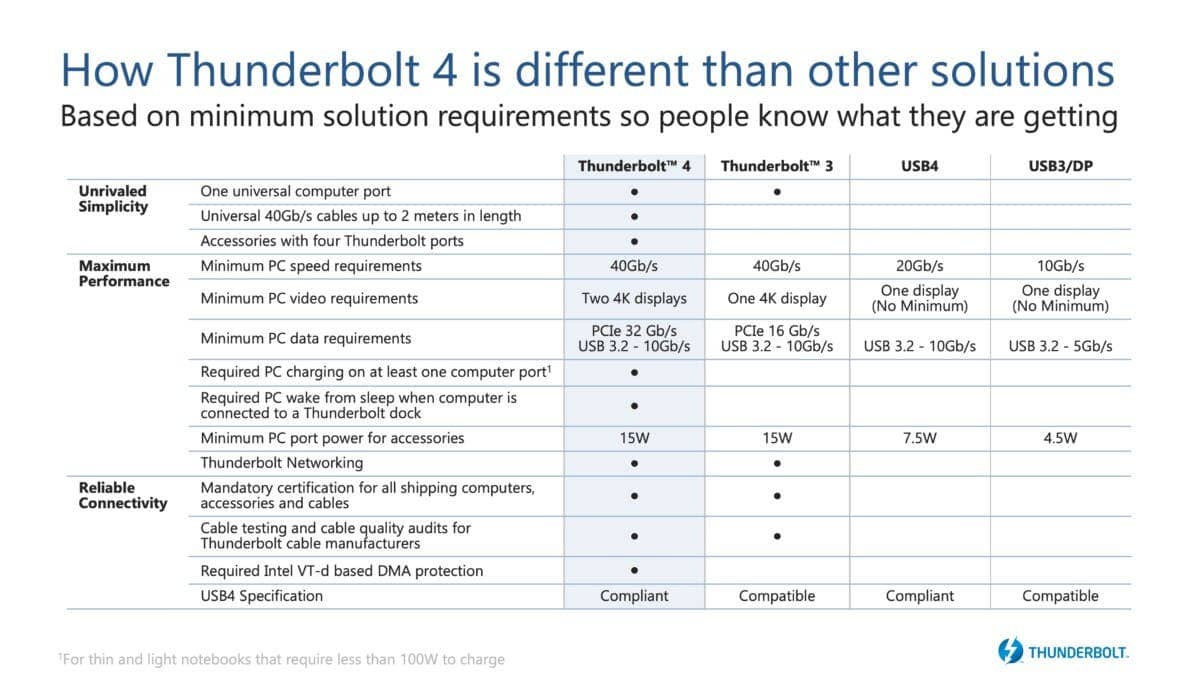
A USB-C cable is often a versatile conduit for data, but it can support various data transfer standards. Here are some of the most crucial ones to help you navigate this landscape:
- USB:
- USB-C can naturally accommodate USB transfer protocols. Importantly, the USB protocol’s speed or generation doesn’t correlate directly with the use of a USB-C port. You can encounter anything from USB 2.0 to USB4 on a USB-C connector.
- USB4, however, brings a significant change. It exclusively employs USB-C connectors, eliminating the Type-A or Type-B formats. This standard boasts an impressive throughput of up to 40 Gbit/s and emphasizes compatibility with other protocols like HDMI and DisplayPort.
- Thunderbolt:
- Manufacturers may also provide Thunderbolt 3 or Thunderbolt 4 options for data transfers. Thunderbolt is an Intel technology popular for offering specifications superior to USB. Thunderbolt 4 represents the most comprehensive iteration possible within the USB-C framework. It’s essentially a guarantee for consumers that they have all the necessary capabilities. However, it’s worth noting that implementing Thunderbolt tends to incur additional costs for manufacturers, and it’s typically reserved for high-end products.
In summary, USB-C is a versatile platform for data transfer, but it can support a range of different protocols, including USB and Thunderbolt. The introduction of USB4 and the exclusive use of USB-C connectors within this standard have ushered in new possibilities for high-speed data transfer and improved compatibility with various protocols. Thunderbolt, on the other hand, offers even greater capabilities but is often associated with premium, high-end products due to the associated manufacturing costs.
Like USB4, Thunderbolt 3 and 4 only exist through the USB-C connector.
Audio and Video Capabilities of USB Type-C
Embedded within the USB Type-C specification is a noteworthy feature, particularly if you have an interest in audio and video: Alternate Mode. This aspect of the specification enables the transmission of various video and audio protocols through USB Type-C. This alternative mode, in contrast to the primary mode (typically used for data transfer, as with USB), facilitates the transmission of several protocols, as demonstrated below.
DisplayPort:
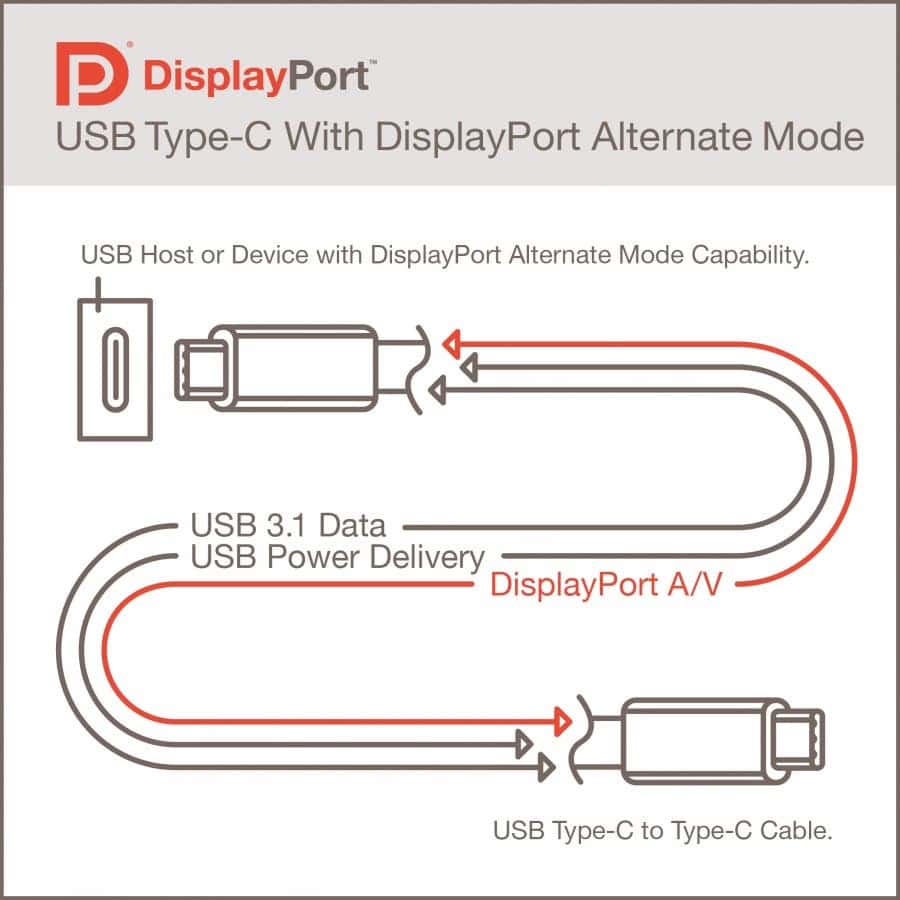
USB Type-C has had the capability to carry a DisplayPort 2014.1 signal since late in version 3 of the specification, thanks to Alternate Mode. With DisplayPort 1.3 support, it becomes possible to connect either two 4K displays at 60 frames per second or a single 5K display. This feature opens up opportunities for high-quality video output and display flexibility through USB Type-C connections.
VESA, the organization responsible for the DisplayPort standard, has introduced support for DisplayPort 1.4 through USB Type-C. This advancement enables the provision of an 8K video stream (with a resolution of 7680 × 4320 pixels, surpassing 33 million pixels compared to 8 million pixels for 4K UHD) at a smooth 60 frames per second. Additionally, it offers support for 4K resolution at a speedy 120 frames per second.
With the arrival of USB-C 2.1, Alternate Mode also incorporates DisplayPort 2.0. This means that USB-C 2.1 has the capability to handle up to three 8K screens (each with a resolution of 7680 x 4320 pixels) at 120 Hz and 10-bit encoding (which includes support for High Dynamic Range or HDR). Alternatively, it can manage a single 16K screen at 60 Hz with 10-bit encoding, demonstrating the exceptional video capabilities of this USB-C version.
HDMI
Moving on to HDMI, the USB Type-C connector can also transport HDMI signals. This is achieved through an alternate mode for USB-C, allowing the transmission of HDMI 1.4b signals. However, it’s worth noting that this mode is limited to Full HD resolution at a maximum of 120 Hz or 4K resolution at 30 Hz, making it suitable for certain video applications but not as advanced as DisplayPort in terms of high-resolution and high-frame-rate video.
A word of caution: It’s quite common for cables or adapters to utilize USB-C’s Alternate Mode for DisplayPort to provide an HDMI port. This become possible through active signal processing, allowing users to connect HDMI-compatible devices to their USB-C ports, providing additional versatility and compatibility.

Audio
Regarding audio, the versatile USB Type-C connector isn’t limited to video alone. It’s also capable of transmitting an audio signal using the USB Audio standard, which is more comprehensive than its predecessor. This feature proves especially practical on smartphones when you need to access a wired audio signal, offering flexibility in audio connectivity.
Energy
Lastly, a critical aspect of the USB Type-C connector is its device power management capabilities. This component plays a crucial role in managing the power supply and distribution within devices, contributing to efficient and adaptable power delivery.
Originally, the USB standard had limitations, providing a modest 2.5W of power (5V at 500 mA). However, with the introduction of Power Delivery, designed primarily for charging mobile devices, the USB landscape evolved significantly. USB-C 2.1, for instance, now allows the connector to deliver an impressive 240W through Power Delivery. Achieving this level of electrical power does necessitate the use of specialized cables and compatible devices.
The advantage of this evolution is the ability to charge a wide range of devices using a universal connector. This includes not only smartphones and headphones but also more power-hungry devices like PCs and mixed reality headsets. Importantly, there’s generally no risk in connecting a low-power device to a high-power charger when using this universal connector. This is because the USB Power Delivery protocol mandates that the device and charger negotiate the appropriate charging power to be in use. Consequently, a Bluetooth headset designed to charge at 10W will never request more power, even when connected to a 100W charger. This negotiation process ensures safe and efficient power delivery for various devices.

Identifying a USB-C Cable or Port
Identifying the capabilities of a USB-C port on a laptop or USB-C cable can indeed be challenging. Fortunately, USB-IF has implemented signage to help users better understand the capabilities of a port.

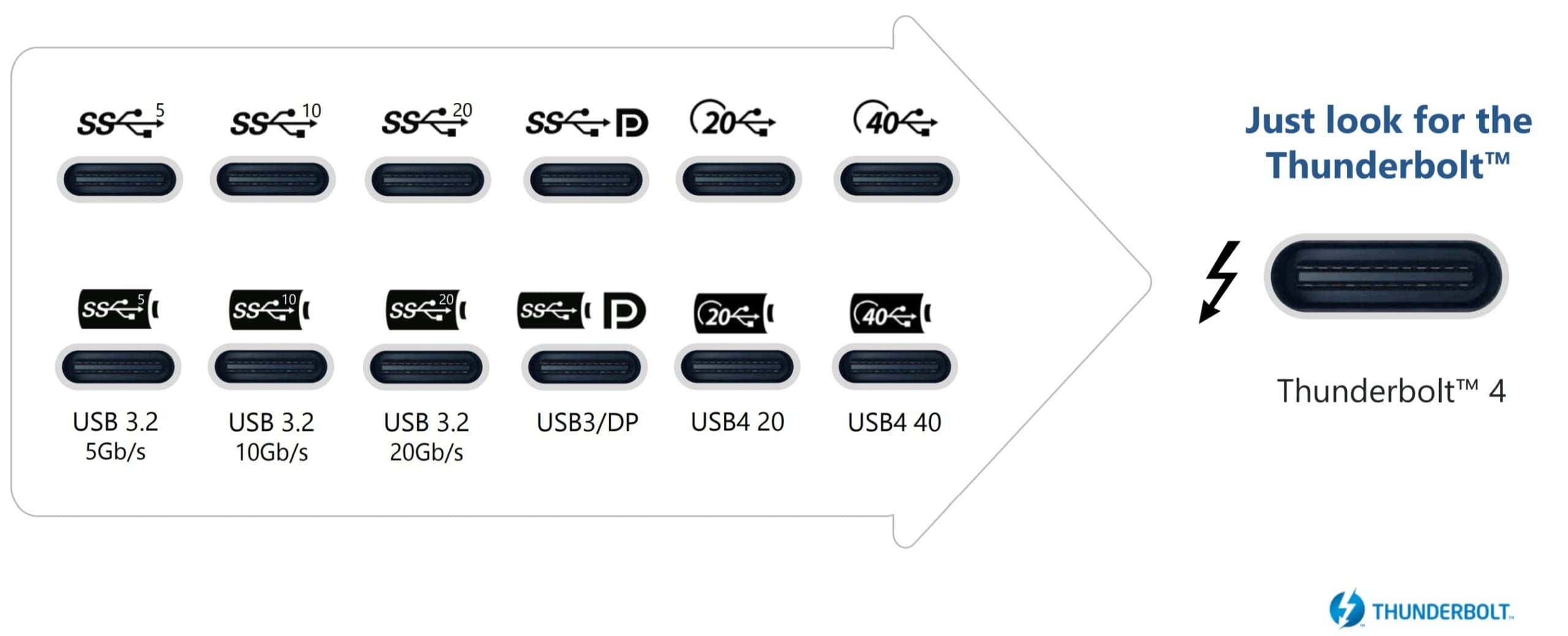
Here are some ways to identify a USB-C port:
- USB-IF Certification Logo: Look for the USB-IF certification logo, a symbol that indicates compliance with USB standards. This logo typically features a USB icon next to the letters “SS” (for SuperSpeed) or “PD” (for Power Delivery), denoting high-speed data transfer or power delivery capabilities.
- Thunderbolt Symbol: If you’re specifically searching for a Thunderbolt port, keep an eye out for the Thunderbolt symbol, which resembles a lightning bolt. Be cautious not to mistake this for a port designed solely for electrical charging.
- Port Labels: Some laptops and devices label their USB-C ports with icons or text to indicate their functions. These labels may include “DP” for DisplayPort, “TB” for Thunderbolt, or “PD” for Power Delivery.
- Color Coding: While less common, some USB-C ports and cables may feature color-coding. For instance, Thunderbolt ports on Apple devices are often marked with a black outline to distinguish them from regular USB-C ports.
- Documentation: Check the user manual or documentation provided with your device or cable. Manufacturers often include information on the capabilities of their USB-C ports and cables.
By paying attention to these indicators, you can more accurately identify the capabilities of USB-C ports and cables. Ensuring that you use them appropriately for your specific needs.





