Cross-Flight Programme With NASA Extended By Russia Until 2025
TechThursday, 28 December 2023 at 15:18
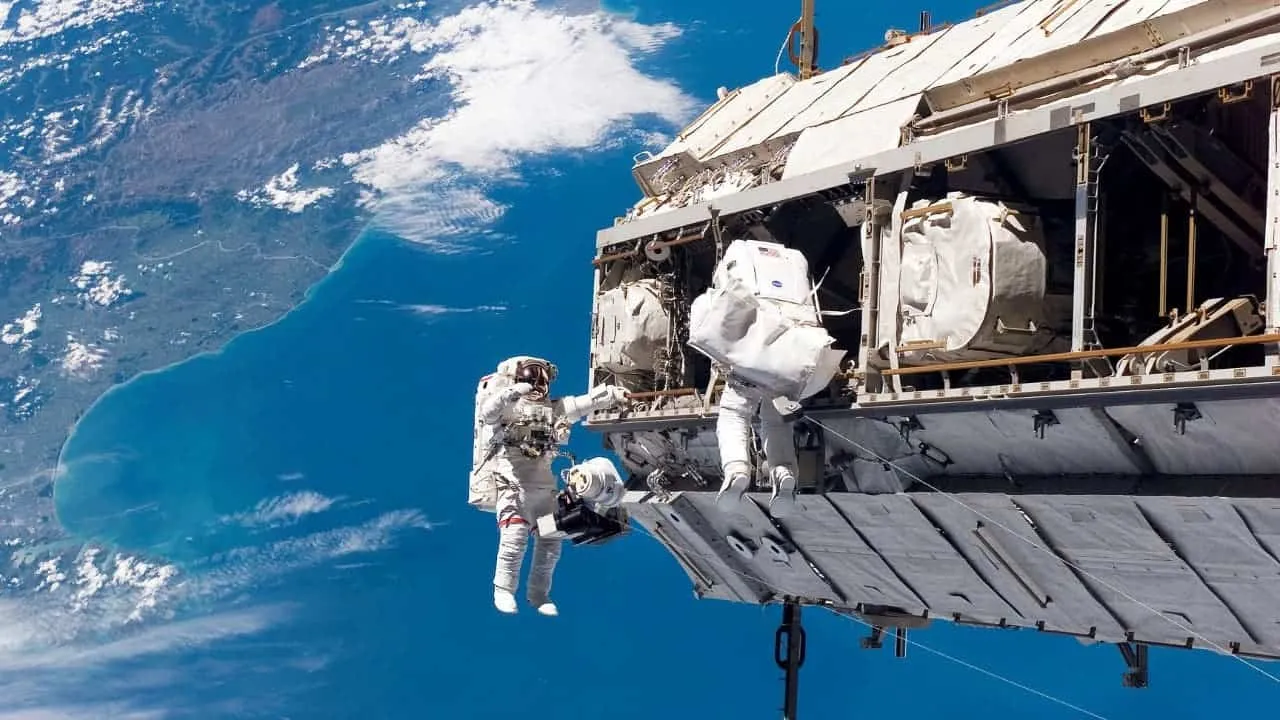

Russia's space state agency, Roscosmos has announced that it will extend its cross-flight programme with NASA to the International Space Station (ISS) until 2025. The programme has been in place since 2011 and has allowed Russian cosmonauts and American astronauts to travel to the ISS on each other's spacecraft. The programme allows Russian cosmonauts to travel to the ISS on American spacecraft and American astronauts to travel to the ISS on Russian spacecraft. Since the start of the programme 12 years ago, it has been extended several times. The latest extension will allow the two countries to continue to work together on the ISS and to share resources and expertise. The U.S. has been banning Russia on several fronts and many American companies even pulled out of Russia. However, on the ISS, both countries managed to continue their cooperation.

Significance of the Programme Extension
The extension of the cross-flight programme between Russia and NASA is significant for several reasons. First, it allows the two countries to continue to work together on the ISS. This is a critical research platform for studying the effects of long-term spaceflight on the human body. It is also relevant for conducting experiments in microgravity. Second, it demonstrates that Russia and the United States can still work together on space projects despite political tensions. Finally, it ensures that the ISS will continue to be staffed with a multinational crew, which is essential for maintaining the station's operations and conducting research.
Conclusion
The cross-flight programme between Russia and NASA to the ISS has been extended until 2025. This is a significant development in the space industry. It allows the two countries to continue to work together on the ISS and to share resources and expertise. It also demonstrates that Russia and the United States can still work together on space projects despite political tensions. Finally, it ensures that the ISS will continue to be staffed with a multinational crew. This is essential for maintaining the station's operations and conducting research.
Loading