Apple Data Protection Officer Gary Davis said in a recent interview with iCulture that he is worried about hackers taking advantage of vulnerabilities after the new European rules. Recall that Apple had to make some changes to its ecosystem to comply with the European Digital Markets Act (DMA). To see some of the changes that Apple made, click here. Mr Davis said that he is afraid that it may become cheaper to attack iPhone users.
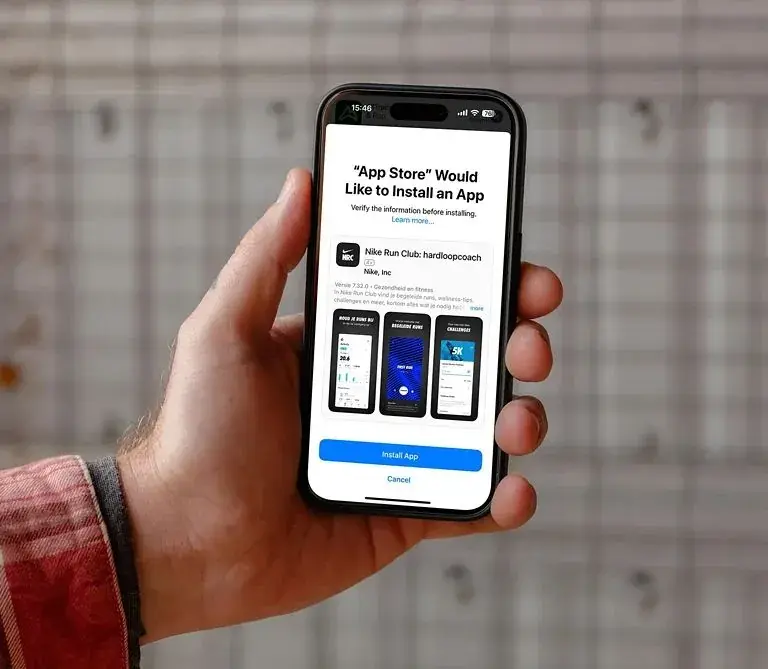
Excerpts of the interview with Davis reads
Our concern is that the “cost” of attacking iOS systems is reduced as a result, which we clearly stated in the white paper. Hackers can attack iPhone users through third-party marketplaces or other payment methods. This means we need to face the types of attacks we have never encountered before.
Overall, the cost of developing iOS vulnerabilities remains high, and our team at Security Labs is working hard to increase the cost of attack so that it is not worthwhile for attackers to target iOS.
This is our current concern. We just don’t know how it will play out. Therefore, we display a special screen with additional information to users who download applications from these third-party sources. Coupled with the notarization process, we hope users can maintain the same confidence.
Apple’s App Store Changes in Europe: A Gateway for Hackers?
Apple’s recent move to implement significant changes in its App Store in Europe has sparked a wave of controversy and concerns regarding potential security risks and increased vulnerability to hacking. The overhaul, driven by the Digital Markets Act (DMA) in the European Union, aims to introduce more competition and consumer choice by allowing users to download iPhone apps from stores other than Apple’s and providing alternative payment methods. However, amidst these intentions lie Apple’s apprehensions and warnings about the security implications of these changes.
For the EU, the new European rules are necessary to prevent monopolistic behaviours by high companies. They want fair competition in the European region which is great for the market. However, some of the changes mean more work for Apple. Since users can now get apps from third-party sources, Apple will now have to put measures in place to protect users. No doubt, it opens up a gateway for hackers, however, users who will be careful will not be affected. Android has been open for years and somehow, users are still protected. Users only need to be careful about the sources from which they get their apps.
Regulatory Clampdown and Security Risks
The DMA-mandated alterations have led Apple to express fears of unnecessary security risks for iPhone users in Europe. The company argues that these changes could expose users to more scams, malicious attacks, and prohibited content from apps downloaded outside its ecosystem. Its emphasis on maintaining security safeguards while complying with the new rules highlights the delicate balance between openness and security in the digital landscape.
Apple’s Security Measures and Market Dynamics
Apple’s staunch security measures, a cornerstone of its brand often get mix-reactions with praise and questions. The company’s “walled garden” approach, rooted in maintaining control over hardware and software, has been pivotal in its success but faces challenges in an evolving digital landscape. The ongoing battle between security, competition, and consumer choice reflects broader industry dynamics and the complexities of regulatory interventions.
Geopolitical Implications and User Protection
Apple’s focus on security, particularly in the face of potential hacking threats, places it in a challenging geopolitical position. The company’s efforts to defend users from sophisticated cyber threats, including those targeting high-profile individuals like activists and journalists, underscore the critical role of technology in safeguarding privacy and freedom of communication. The intersection of security, privacy, and government scrutiny raises questions about the balance of power and responsibility in the digital age.
Future Outlook and Global Impact
As Apple navigates the changing regulatory landscape in Europe and beyond, the implications of these App Store changes extend far beyond the company itself. The broader tech industry, including competitors like Google and Facebook, is also adapting to new regulations that challenge established norms of control and competition. The evolving relationship between tech giants, regulators, and consumers underscores the ongoing debate over security, privacy, and innovation in a rapidly changing digital world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Apple’s response to new European rules reshaping its App Store reflects a complex interplay of security concerns, competition dynamics, and regulatory pressures. While the push for increased consumer choice and competition is laudable, the potential security risks and industry tensions highlight the delicate balance between openness and protection in the digital ecosystem. As Apple and other tech giants navigate these challenges, the future of digital innovation and security remains a critical and evolving landscape.





