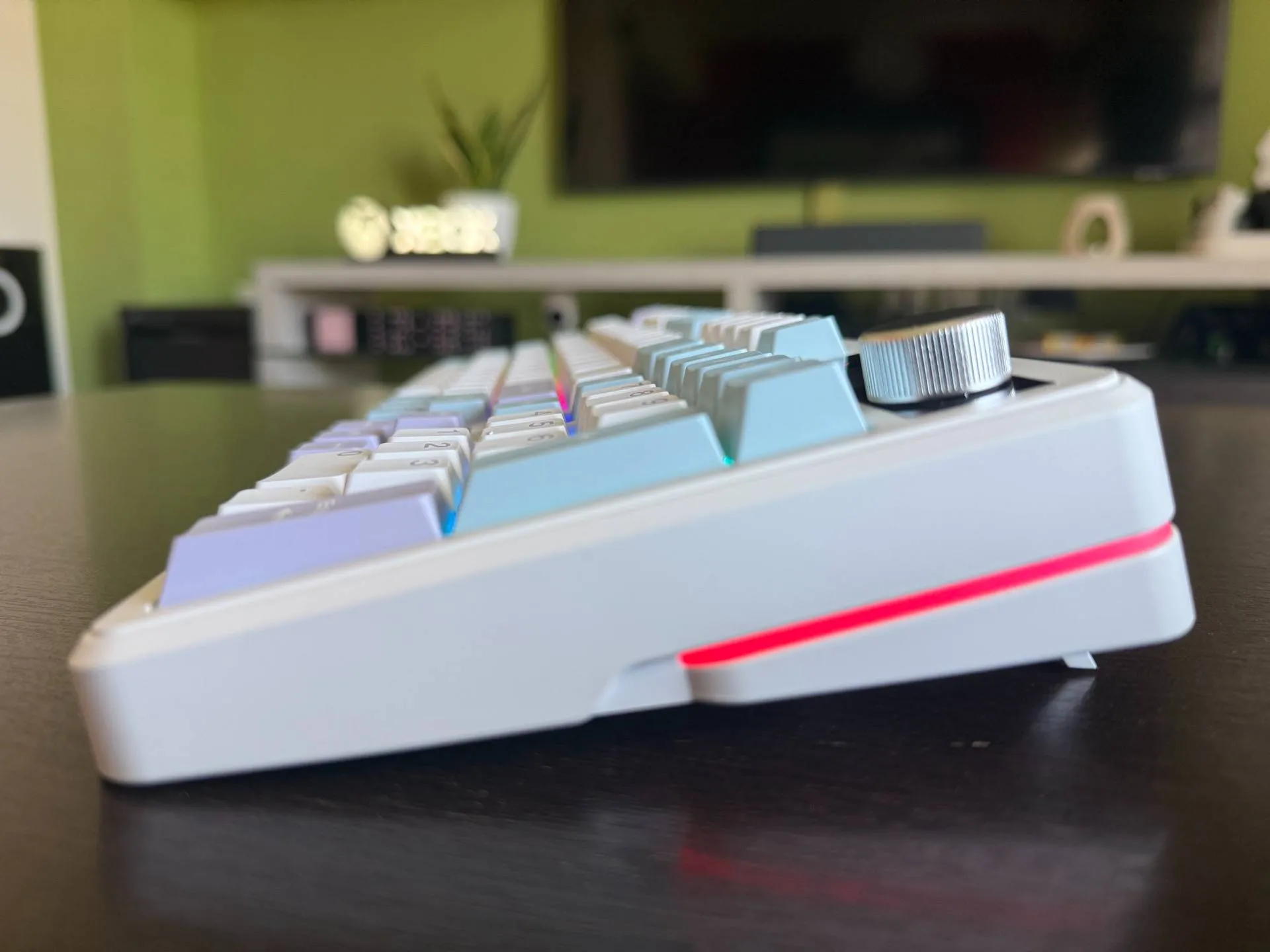
Epomaker TH99 Pro Review: The Best Mechanical Keyboard for Under $90?
Mar 12, 12:52
Xiaomi Mix Fold 5 Leaks Point to Magnetic Modular Camera and New Hinge Design
Mar 13, 08:49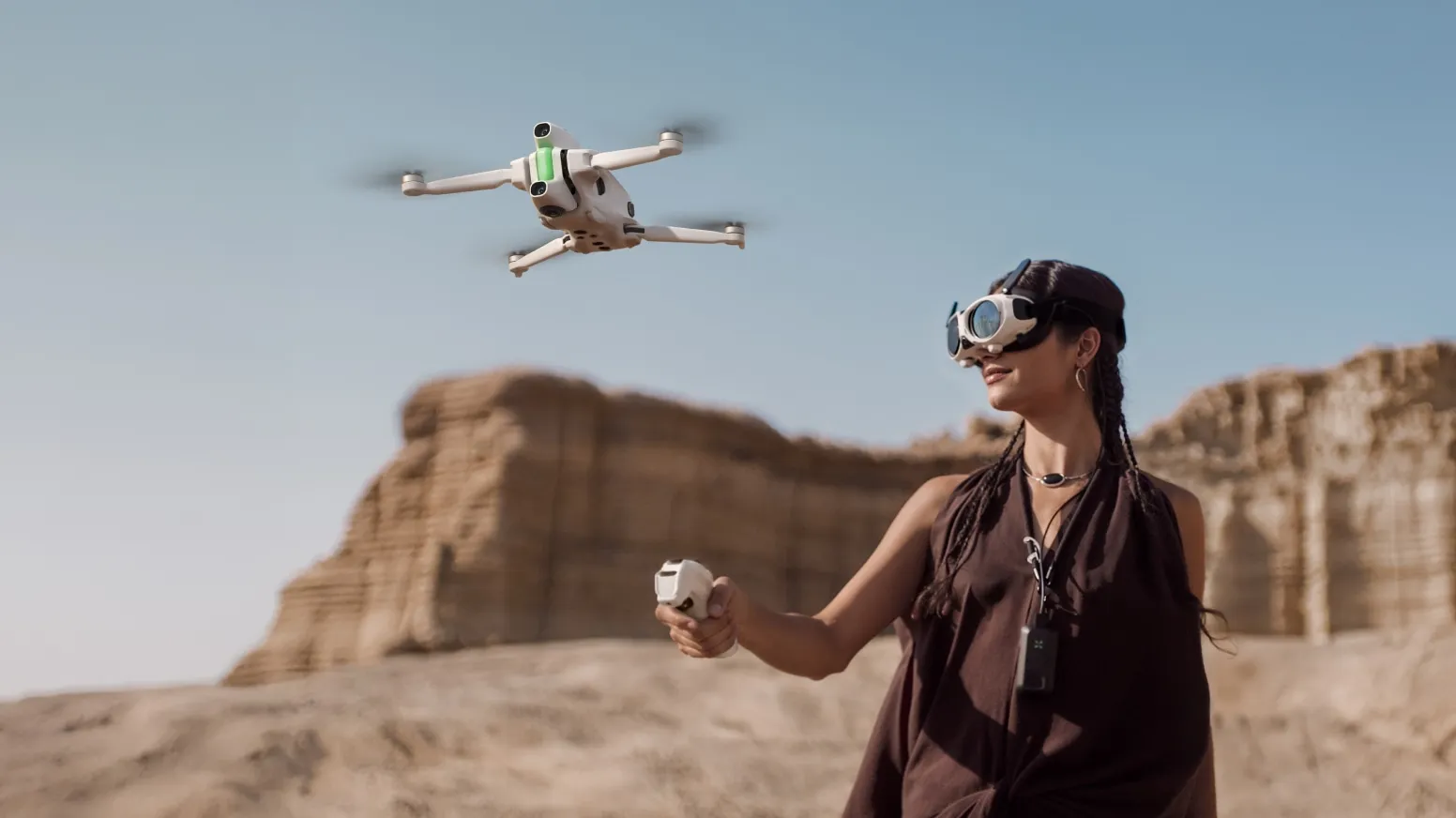
The Best Drones of 2026 So Far: Top Picks for Photography, Video, and FPV
Mar 13, 05:29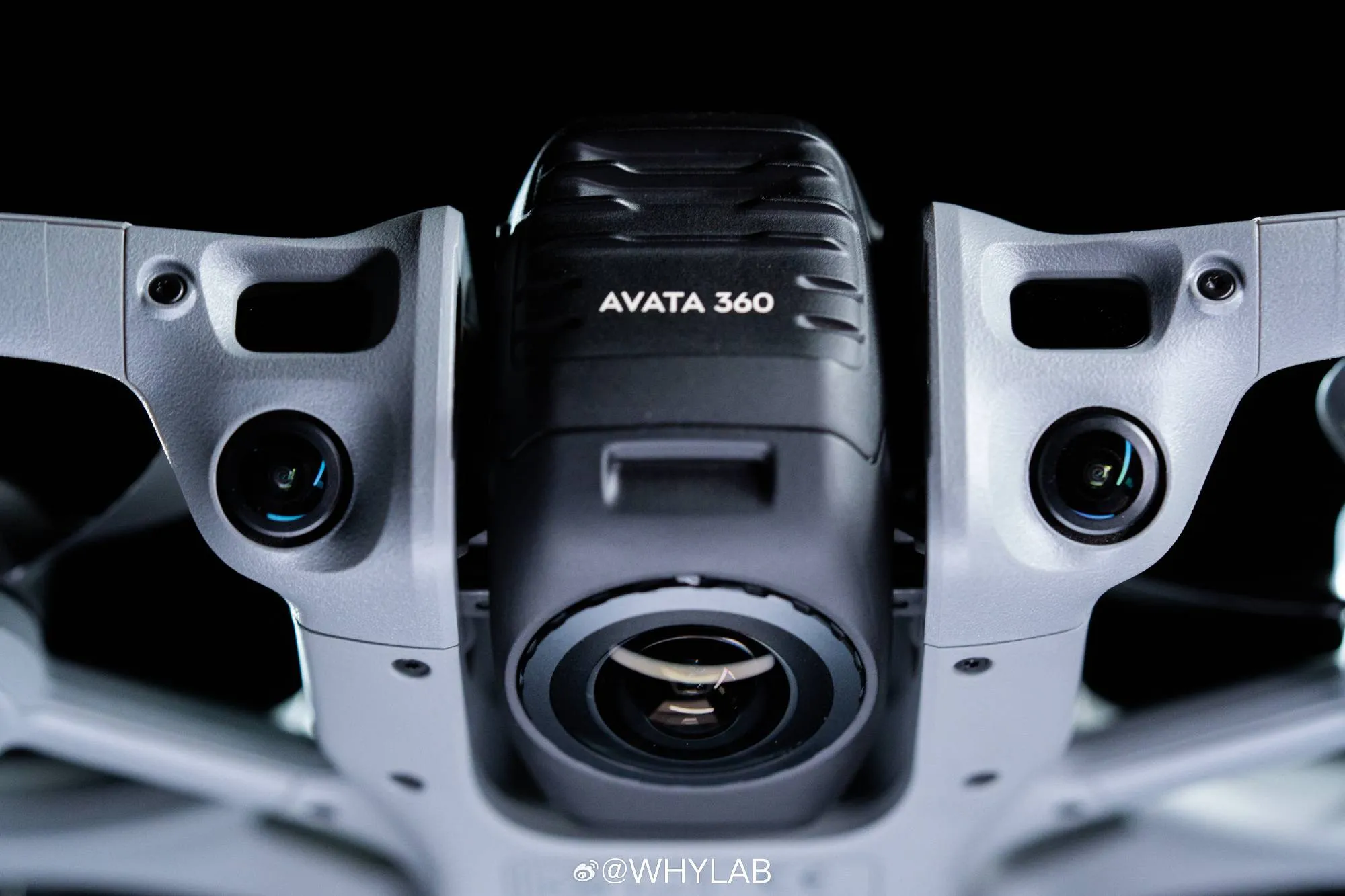
DJI Avata 360, the Company's 8K Panoramic Drone Revealed With Launch Date
Mar 12, 21:49
Xbox Project Helix: Next-Gen Console Built With AMD and DirectX
Mar 12, 10:34
Vivo Patents a Rollable Phone That Gets Taller, Not Wider
Vivo filed a patent for a vertically expanding rollable phone — a design that makes the screen taller rather than wider, flipping the rollable concept.
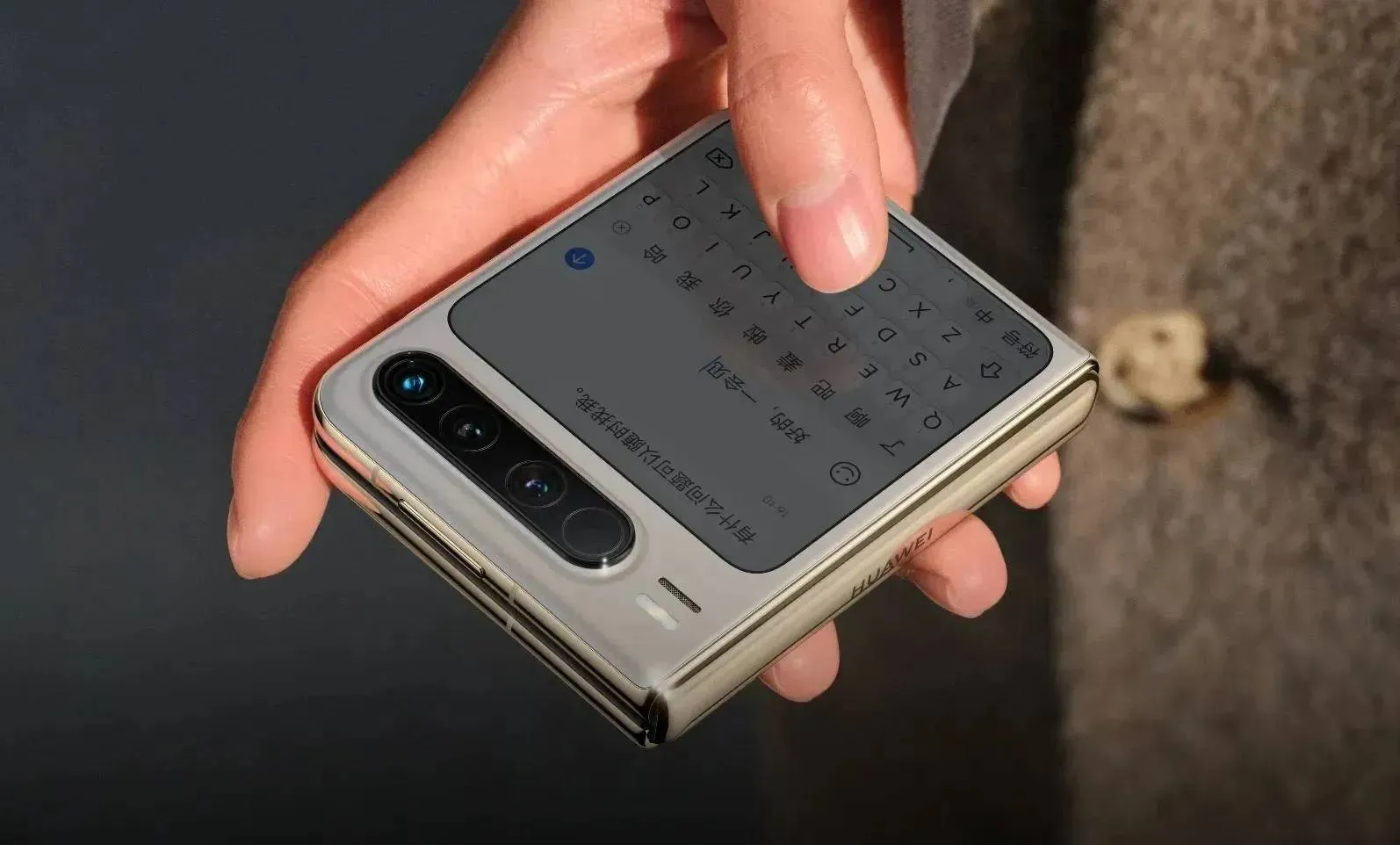

Huawei Is About to Drop a Lot of Products — Here's What's Coming
Huawei is launching the Enjoy 90 series, Pura X2, Pura 90, and a new HarmonyOS version in a two-wave product push covering five device categories.
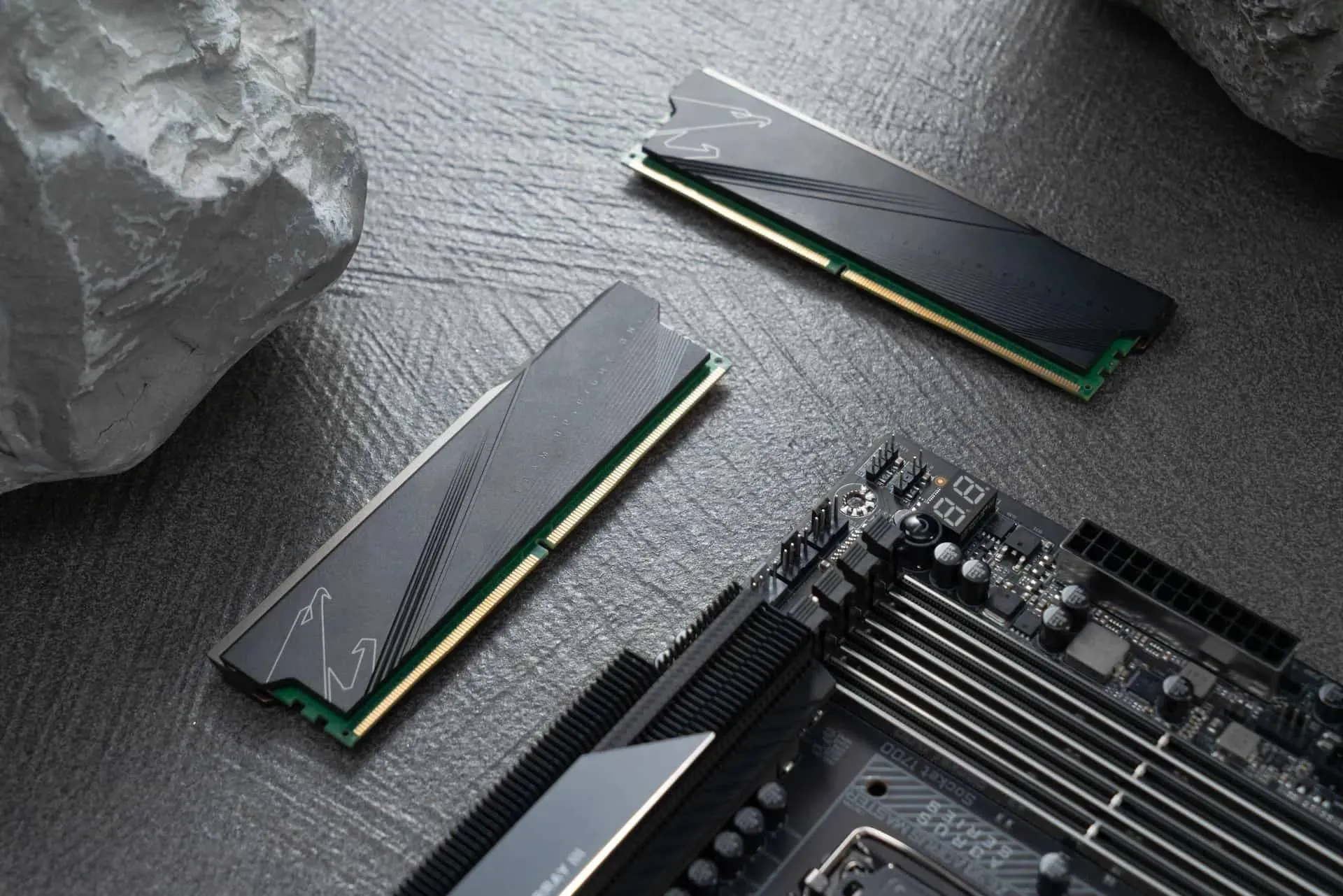

DDR5 Memory Price Surge Leads to Consumer Warranty Disputes
DDR5 prices have surged 4x in two years — and now consumers filing warranty claims are being asked to pay hundreds extra for identical replacements.

Volkswagen and XPeng Start Mass Production of Their First Joint Car
Volkswagen confirms its first jointly developed vehicle with XPeng has entered mass production — a key milestone in VW's China market recovery plan.
- Great insights on the Honor Watch GS 5 features! The 23-day battery life and advanced health tracking tools make it a strong competitor in the wearable market. At Hezire Technologies, we’re also seeing growing interest in smart wearables that offer long battery performance and accurate health data feedback. Users in Dubai and the UAE are always asking for reliable devices that support active lifestyles — and watches like the GS 5 really fit that need. Thanks for the detailed specs!
 heziretechnologies19-02-2026
heziretechnologies19-02-2026 - I want to know how much the Oppo Pad 4 Pro tablet is currently priced please?Egyptian13-02-2026
- I want to know how much is the price of the Oppo Pad 4 Pro tablet currentlyEgyptian13-02-2026
- We hope that the giant Xiaomi will put a cooling fan in the global version of the Xiaomi 17T Pro phone as in the Redmi K90 Ultra, albeit with less capabilities, and that the battery will be larger than 7500 mAh, and the screen will reach 6.85 inches.Egyptian12-02-2026
- Most of the tablets doesn't support Zoom video blur background feature.YugeshM1509-02-2026
- 👍️CajunMoses03-02-2026
- Besoin de ça
 merveil11-12-2025
merveil11-12-2025 - Looking forward to buying both sizes of this when they are available in Thailand 🇹🇭chrisman08-12-2025
- Finally! Surprised corrupt Grok was not mentionedMaxNix07-12-2025
- About time!!MaxNix07-12-2025

DJI Avata 360, the Company's 8K Panoramic Drone Revealed With Launch Date
DJI unveiled the Avata 360 — its first 8K panoramic flagship drone with a rounded matte silver body, orange motor accents, and enclosed prop guards.
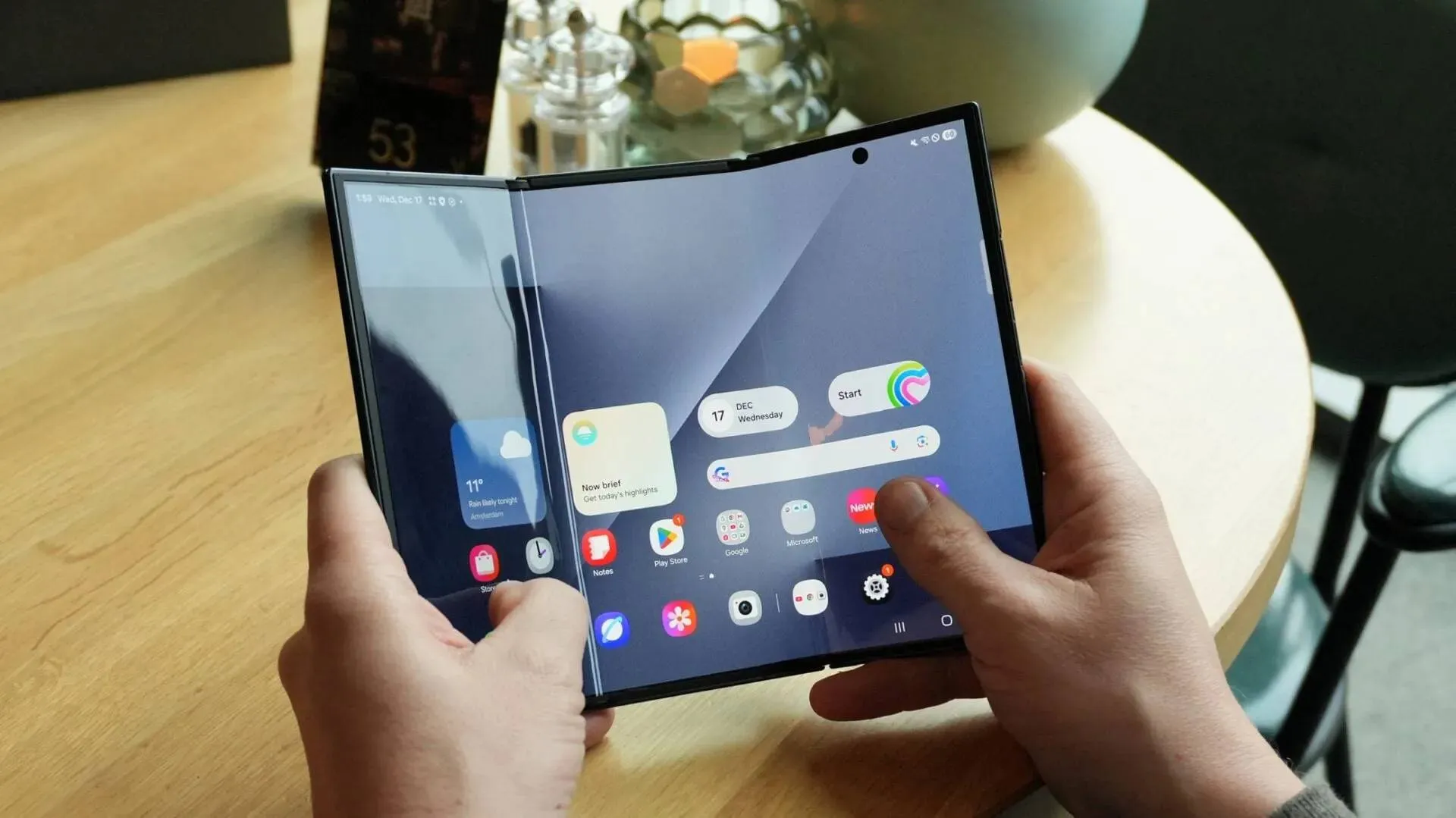

Wide-Screen Foldables and Super-Large Air Models Launch Q4 2026
Wide-screen foldables and super-large Air models launch 2026. Continuous price increases expected throughout year. Q4 phone trends detailed.
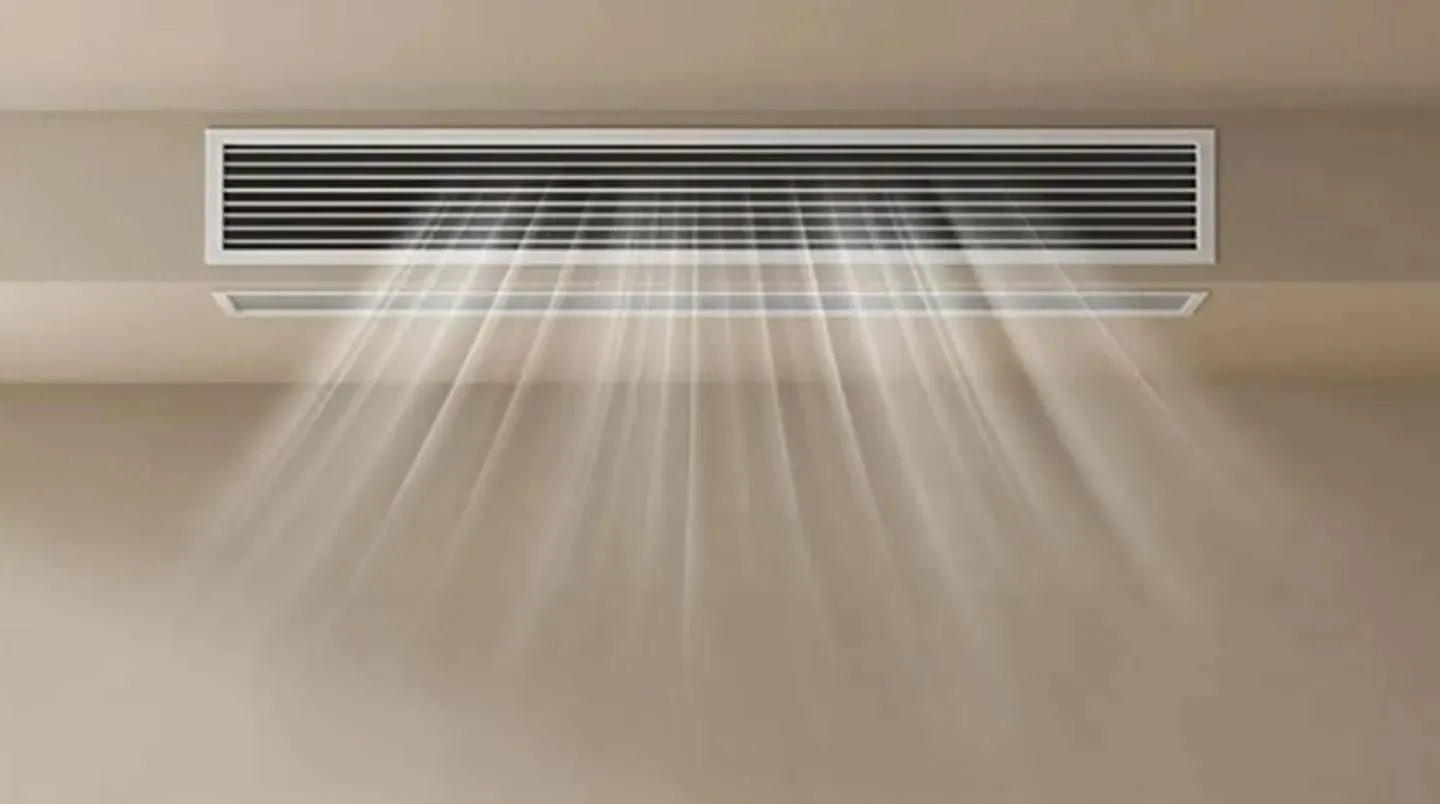

Xiaomi Launches New Mijia Powerful Air Duct Air Conditioner with High-Performance Specs
Xiaomi's Mijia Powerful Air Duct AC delivers 10,600W cooling, 15,000W heating, a Sanyo compressor, and a 10-year free repair warranty from 5,524 RMB (~700 Euros).
Top 6 WhatsApp settings to turn on to keep your account safe and how to activate them
WhatsApp is where most of our daily talks happen. Chats with friends, work updates, photos, and even bank alerts all go through it.
Loading